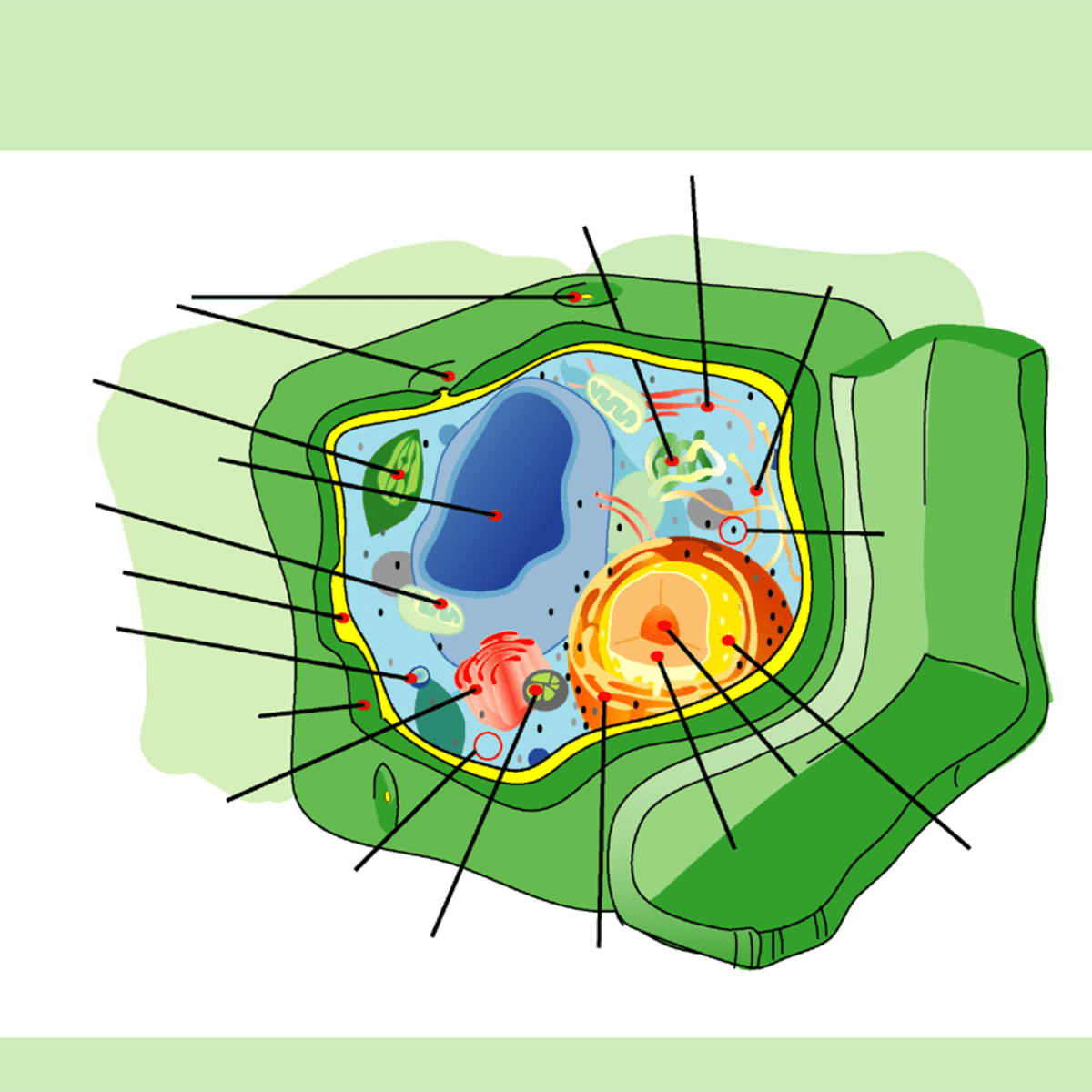
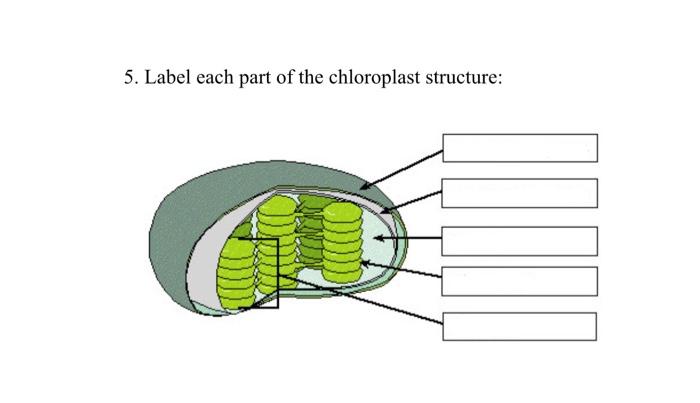
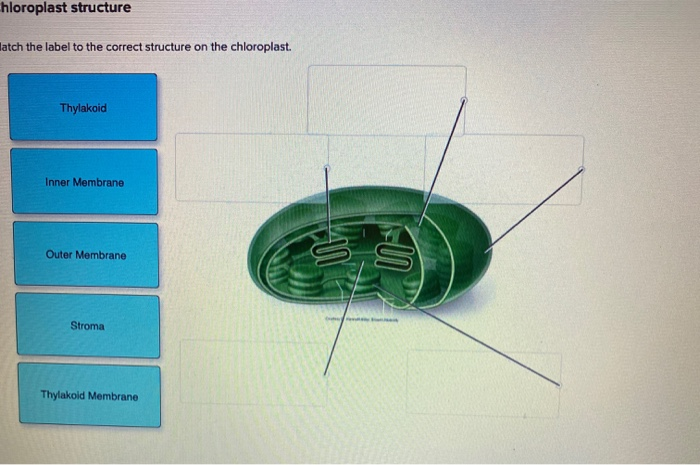
38 label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function
› cells › 3dcellInteractive Cell Models - CELLS alive For life all cells have basic needs. Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements. Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences that have become the characteristics of eukaryote (animal, plant) and prokaryotic (bacteria) cells. › cellsPlant and Animal Cell Worksheets - Math Worksheets 4 Kids The worksheets recommended for students of grade 4 through grade 8 feature labeled animal and plant cell structure charts and cross-section charts, cell vocabulary with descriptions and functions and exercises like identify and label the parts of the animal and plant cells, color the cell organelles, match the part to its description, fill in ...
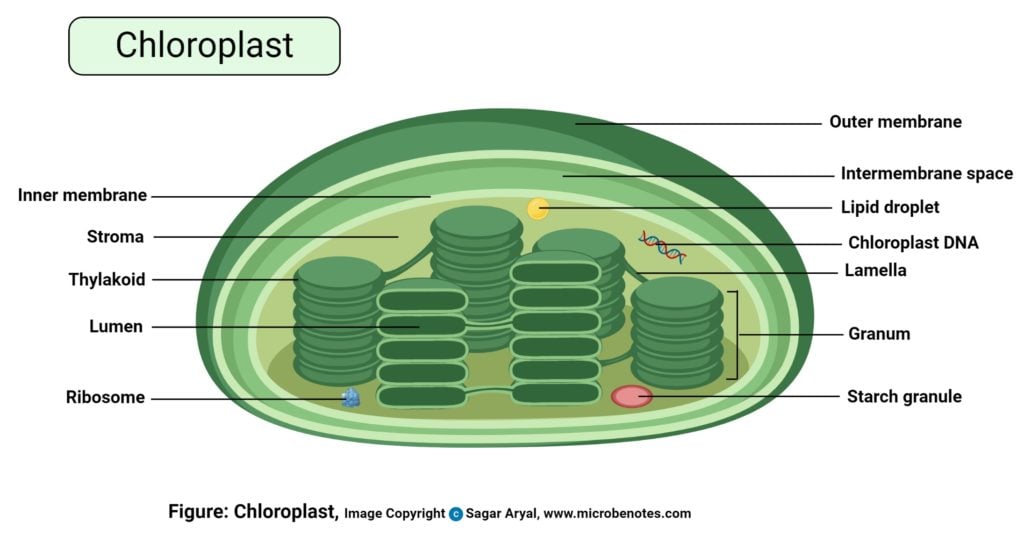
Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram - Microbe Notes Chloroplasts are a type of membrane-bound plastids that contain a network of membranes embedded into a liquid matrix and harbor the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. It is this pigment that imparts a green color to plant parts and serves to capture light energy. Chloroplasts can be found in the cells of the mesophyll in plant leaves.
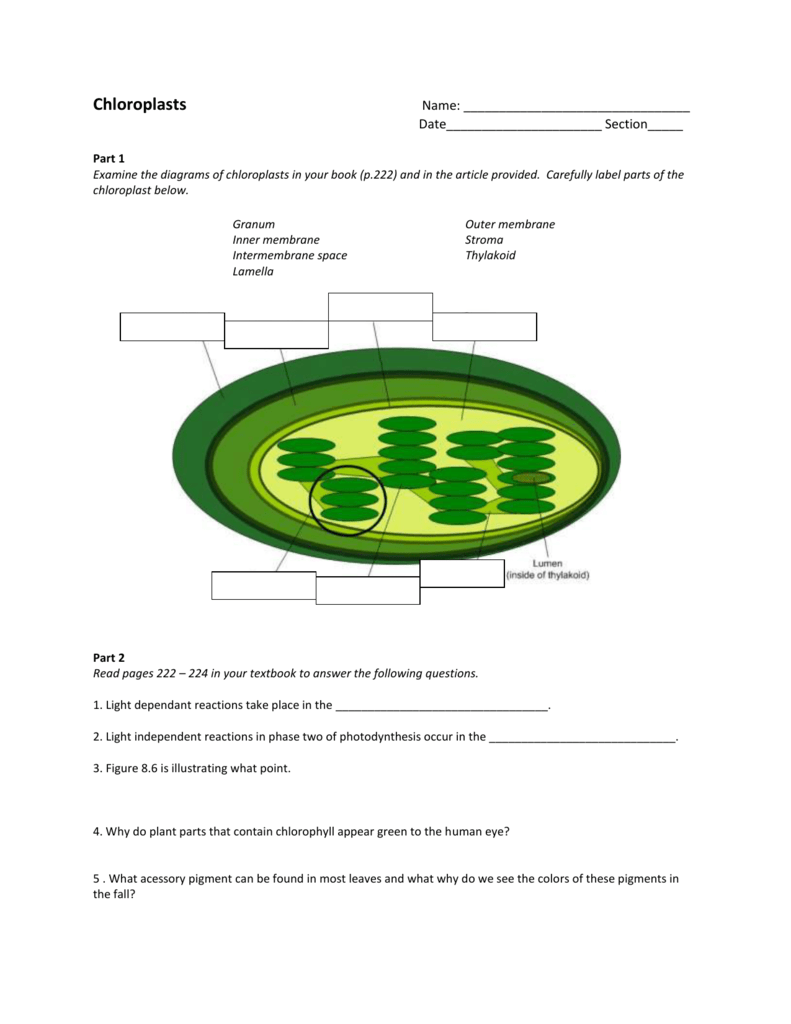
Label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function
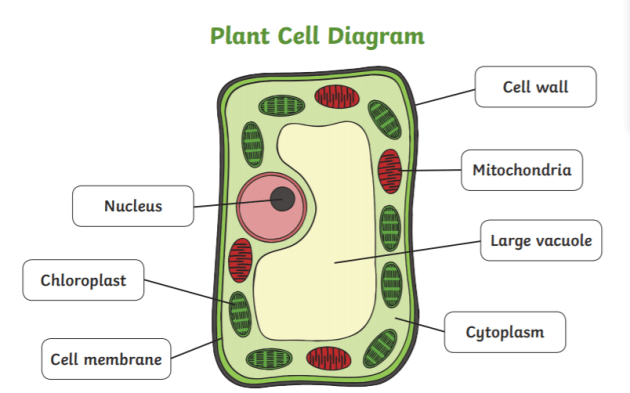
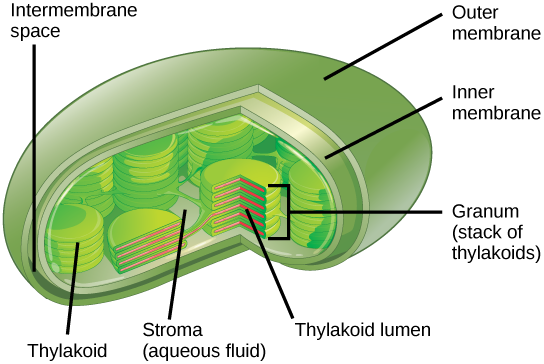
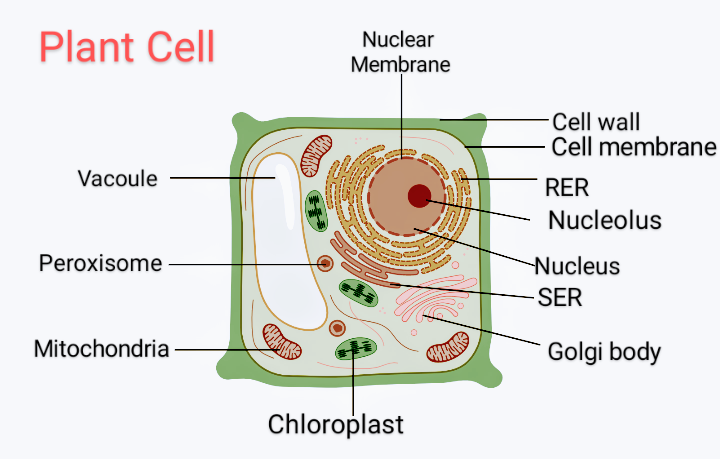
› health › anatomyCell Menu - Games & Tutorials - Sheppard Software Games Learn about the different organelles in animal, bacteria, and plant cells! Colorful animations make these flash games as fun as it is educational Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram It is the rigid outer cover of the plant cell with a major role of protecting the plant cell, giving it, its shape. Structure of plant cell wall It is a specialized matrix that covers the surface of the plant cell. Every plant cell has a cell wall layer which is a major distinguishing factor between a plant cell and an animal cell. Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise The major components of a chloroplast are as illustrated and explained below. Envelope The chloroplast envelope is double-membrane structure comprising an outer and an inner membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer, and is 6 - 8 nm thick. A 10 - 20 nm thick space present between the two membranes is known as intermembrane space.
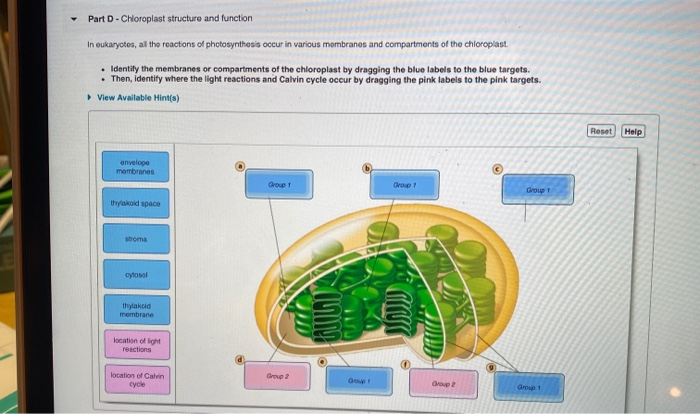
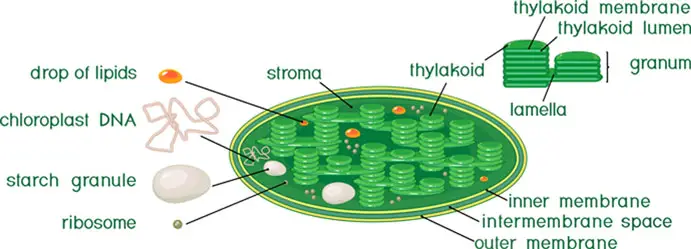
Label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function. Chloroplast: Diagram, Structure, Functions & More - Embibe One of the most important functions of the Chloroplast is to absorb light energy for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts consist of Stroma, inner membrane, outer membrane, thylakoid membrane, and intermembrane space. Chloroplast Analogy An analogy for chloroplasts is that chloroplasts are like a kitchen of the cell. Labeling Chloroplast Diagram | Quizlet inner most cell membrane of chloroplast intermembrane space space between inner and outer membrane outer membrane membrane of chloroplast that is in contact with the cytosol of plant cell stroma liquid portion of chloroplast where Calvin Cycle (dark reactions) take place lumen of thylakoid space inside the thylakoid where light reactions occur. Chloroplast Label Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Browse chloroplast label resources on Teachers Pay Teachers, a marketplace trusted by millions of teachers for original educational resources. Browse Catalog Grade Level Pre-K - K 1 - 2 3 - 5 6 - 8 9 - 12 Other Subject Arts & Music English Language Arts World Language Math Science Social Studies - History Specialty Holidays / Seasonal Price Free Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The main components of a chloroplast are protein (50 to 60%), lipids, pigments like carotenoids and chlorophyll, a small amount of RNA and DNA, traces of Vitamin E and K and minerals iron, magnesium, manganese, etc. A chloroplast is covered by a membranous envelope, inside which matrix and thylakoids are present.
CELLS alive! WebSince 1994, CELLS alive! has provided students with a learning resource for cell biology, microbiology, immunology, and microscopy through the use of mobile-friendly interactive animations, video, puzzles, quizzes and study aids. Chloroplasts - Structure And Functions - A Level Biology The chloroplasts with the nucleus and cell membrane and ER are the key organelles of pathogen defense. The most important function of chloroplast is to make food by the process of photosynthesis. Food is prepared in the form of sugars. During the process of photosynthesis sugar and oxygen are made using light energy, water, and carbon dioxide. Interactive Cell Models - CELLS alive WebFor life all cells have basic needs. Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements. Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences that have become the characteristics of eukaryote (animal, plant) and prokaryotic (bacteria) cells. Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets - Math Worksheets 4 Kids WebThe worksheets recommended for students of grade 4 through grade 8 feature labeled animal and plant cell structure charts and cross-section charts, cell vocabulary with descriptions and functions and exercises like identify and label the parts of the animal and plant cells, color the cell organelles, match the part to its description, fill in ...
Chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram Chloroplasts are a type of plastid—a round, oval, or disk-shaped body that is involved in the synthesis and storage of foodstuffs. Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green colour, which results from the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Bio 2 Exam 1, bio 1407 exam 2, bio exam 4 Flashcards | Quizlet WebLabel each of the following types of natural selection based on the graphs provided. stabilizing 2 ... while the other species spends most of its time on land. This is known as. ... The outer membrane of a mitochondrion and chloroplast resemble a eukaryotic cell while the inner membrane resembles that of a bacterial cell. Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS The chloroplast structure consists of the following parts: Membrane Envelope It comprises inner and outer lipid bilayer membranes. The inner membrane separates the stroma from the intermembrane space. Intermembrane Space The space between inner and outer membranes. Thylakoid System (Lamellae) The system is suspended in the stroma. Cell (biology) - Wikipedia WebThe cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms.Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites. The term comes from the Latin word cellula meaning 'small room'.. Cells can acquire specified …
Chloroplast - Definition, Function and Structure | Biology Dictionary Function of Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are the part of plant and algal cells that carry out photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy to energy stored in the form of sugar and other organic molecules that the plant or alga uses as food. Photosynthesis has two stages. In the first stage, the light-dependent reactions occur.
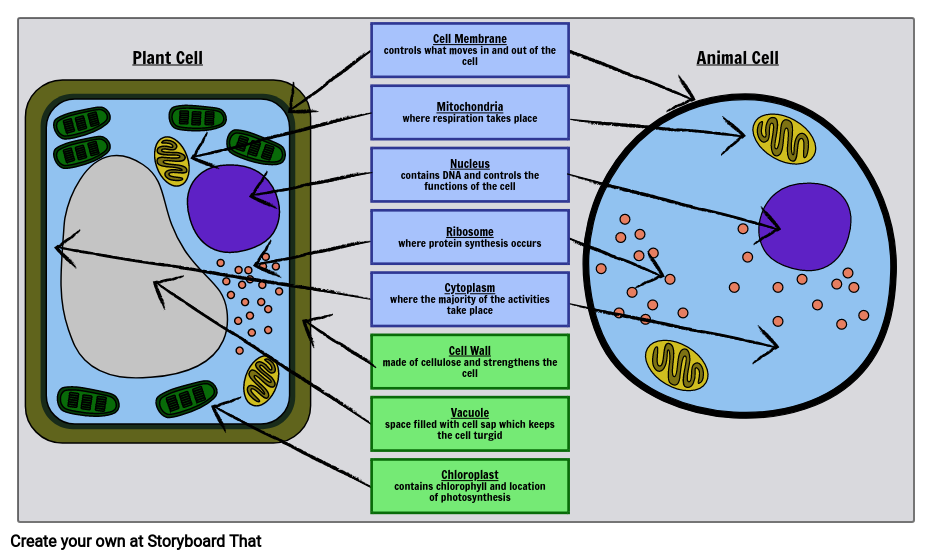
What Is Mitochondria (Structure, Diagram & Function) - BYJUS The mitochondrion is a double-membraned, rod-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cell. Its size ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometre in diameter. The structure comprises an outer membrane, an inner membrane, and a gel-like material called the matrix. The outer membrane and the inner membrane are made of proteins and phospholipid layers ...
Cells Cells - Parts of the Cell Rap - YouTube WebThis rap was created for a 6th-grade science classroom to teach about the different parts of a cell. With its catchy rhythm and rhymes, students of all learn...
Chloroplast Structure, Functions, and Processes - Study.com provides structure and protects the cell. Chloroplast. contains the chlorophyll that makes plants green and is where photosynthesis takes place. Mitochondria. specialized organelles that power the ...
The students will label the parts of the chloroplast and give the function In addition of regulation activity, the fatty acids, lipids and carotenoids are synthesized in the inner chloroplast membrane. 3. Stroma . It contain the enzymes necessary for carbon fixation, it also manages the chloroplast response to cellular stresses and signaling between various organelles. 4. Thylakoid
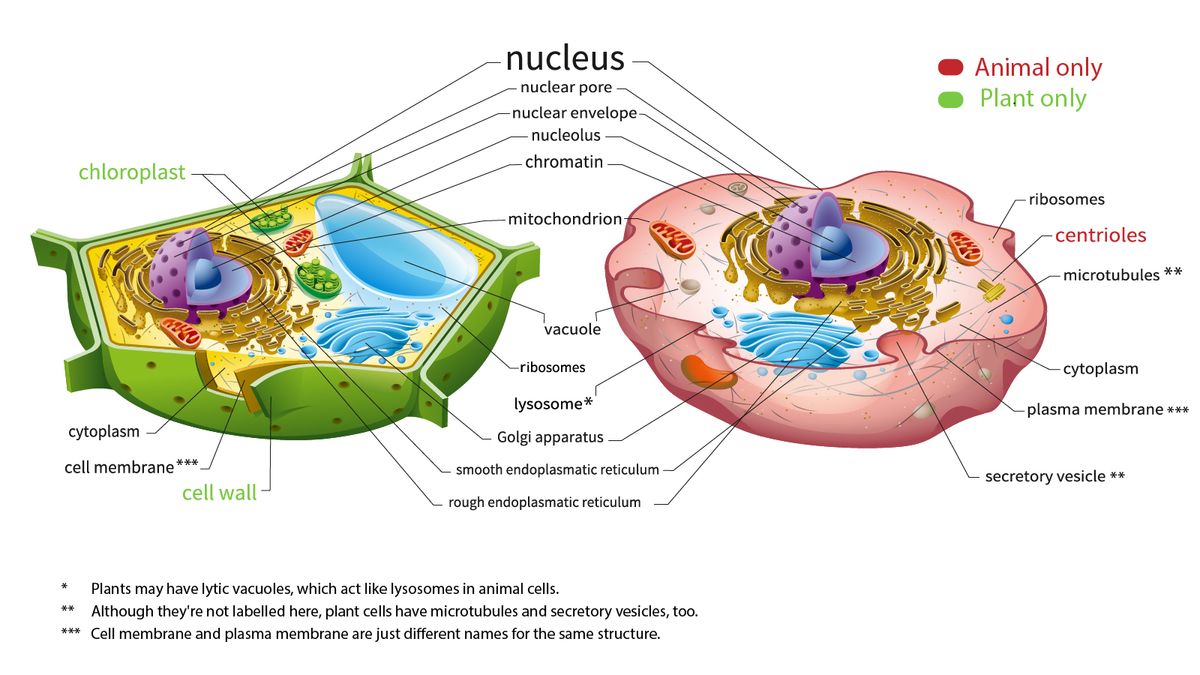
› wuGenglin143 › plant-and-animalPlant and Animal Cells - SlideShare Jul 29, 2016 · Function: It supports and protects the cell. It also controls the movement of materials in/out of cell. It forms a barrier between cell and its environment. Cell Membrane 1. Cell Membrane 7. Common Parts of Animal And Plant Cells It is the fluid substance that fills the cell. All the cell organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm.
CROSS SECTION OF A LEAF [BASIC] - Pathwayz Chloroplasts are found near the palisade cell surface to maximise light absorption and to reduce the distance that carbon dioxide and oxygen have to diffuse (to / from the chloroplast stoma) '''Spongy Mesophyll''': These cells are smaller than those of the palisade mesophyll and are found in the lower part of the leaf. They also contain ...
Chloroplast Quiz - PurposeGames.com The chloroplast converts sulight, water and carbon dioxide into sugar: stored energy. Find the parts. Image by user It'sJustMe in the Wikimedia Commons Remaining 0 Correct 0 Wrong 0 Press play! 0% 0:00.0 Highscores Show More Other Games of Interest Inside A Computer EC Science Creator joefinkelstein Quiz Type Image Quiz Value 15 points Likes 24
Chloroplasts: Definition, Diagram, Structure and Function - Collegedunia The basic functions of the chloroplast are- To synthesize food through the process of photosynthesis. They provide diverse metabolic activities. They serve as cellular sensors They produce Adenosine Triphosphate- ATP through the process of photosynthesis. They absorb the energy of light and convert them into chemical energy.
Cell Menu - Games & Tutorials - Sheppard Software Games WebLearn about the different organelles in animal, bacteria, and plant cells! Colorful animations make these flash games as fun as it is educational
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › GenomeGenome - Wikipedia In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses).The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident ...
alive! Since 1994, CELLS alive! has provided students with a learning resource for cell biology, microbiology, immunology, and microscopy through the use of mobile-friendly interactive animations, video, puzzles, quizzes and study aids.
› watchCells Cells - Parts of the Cell Rap - YouTube This rap was created for a 6th-grade science classroom to teach about the different parts of a cell. With its catchy rhythm and rhymes, students of all learn...
What are the parts of a chloroplast and their functions? Recent studies have shown that chloroplasts can be interconnected by tubular bridges called stromules, formed as extensions of their outer membranes.[7][8] Chloroplasts appear to be able to ...
Genome - Wikipedia WebThe term genome was created in 1920 by Hans Winkler, professor of botany at the University of Hamburg, Germany. The Oxford Dictionary and the Online Etymology Dictionary suggest the name is a blend of the words gene and chromosome. However, see omics for a more thorough discussion. A few related -ome words already existed, such as …
Chloroplast Function & Structure | What is a Chloroplast? - Video ... A chloroplast has five main parts: Outer membrane: This holds everything together and is semi-permeable, so it only allows select molecules to pass through. Inner membrane: The inner membrane...
Plant and Animal Cells - SlideShare WebJul 29, 2016 · Function: It supports and protects the cell. It also controls the movement of materials in/out of cell. It forms a barrier between cell and its environment. Cell Membrane 1. Cell Membrane 7. Common Parts of Animal And Plant Cells It is the fluid substance that fills the cell. All the cell organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm.
Phase transition - Wikipedia WebIn chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma.A phase of a thermodynamic system and the …
Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise The major components of a chloroplast are as illustrated and explained below. Envelope The chloroplast envelope is double-membrane structure comprising an outer and an inner membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer, and is 6 - 8 nm thick. A 10 - 20 nm thick space present between the two membranes is known as intermembrane space.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram It is the rigid outer cover of the plant cell with a major role of protecting the plant cell, giving it, its shape. Structure of plant cell wall It is a specialized matrix that covers the surface of the plant cell. Every plant cell has a cell wall layer which is a major distinguishing factor between a plant cell and an animal cell.
› health › anatomyCell Menu - Games & Tutorials - Sheppard Software Games Learn about the different organelles in animal, bacteria, and plant cells! Colorful animations make these flash games as fun as it is educational






















Post a Comment for "38 label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function"