40 label atp and adp molecules
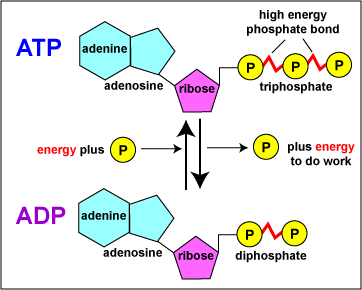
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP. Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg Question: 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6.
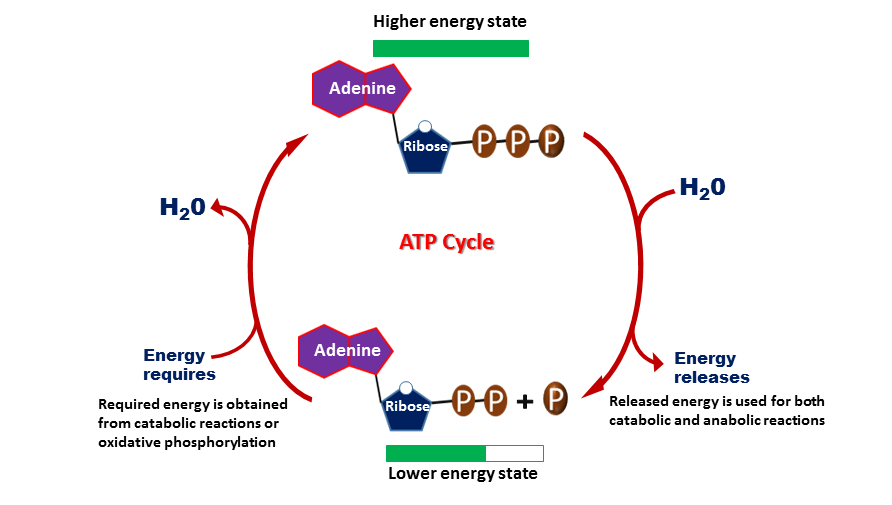
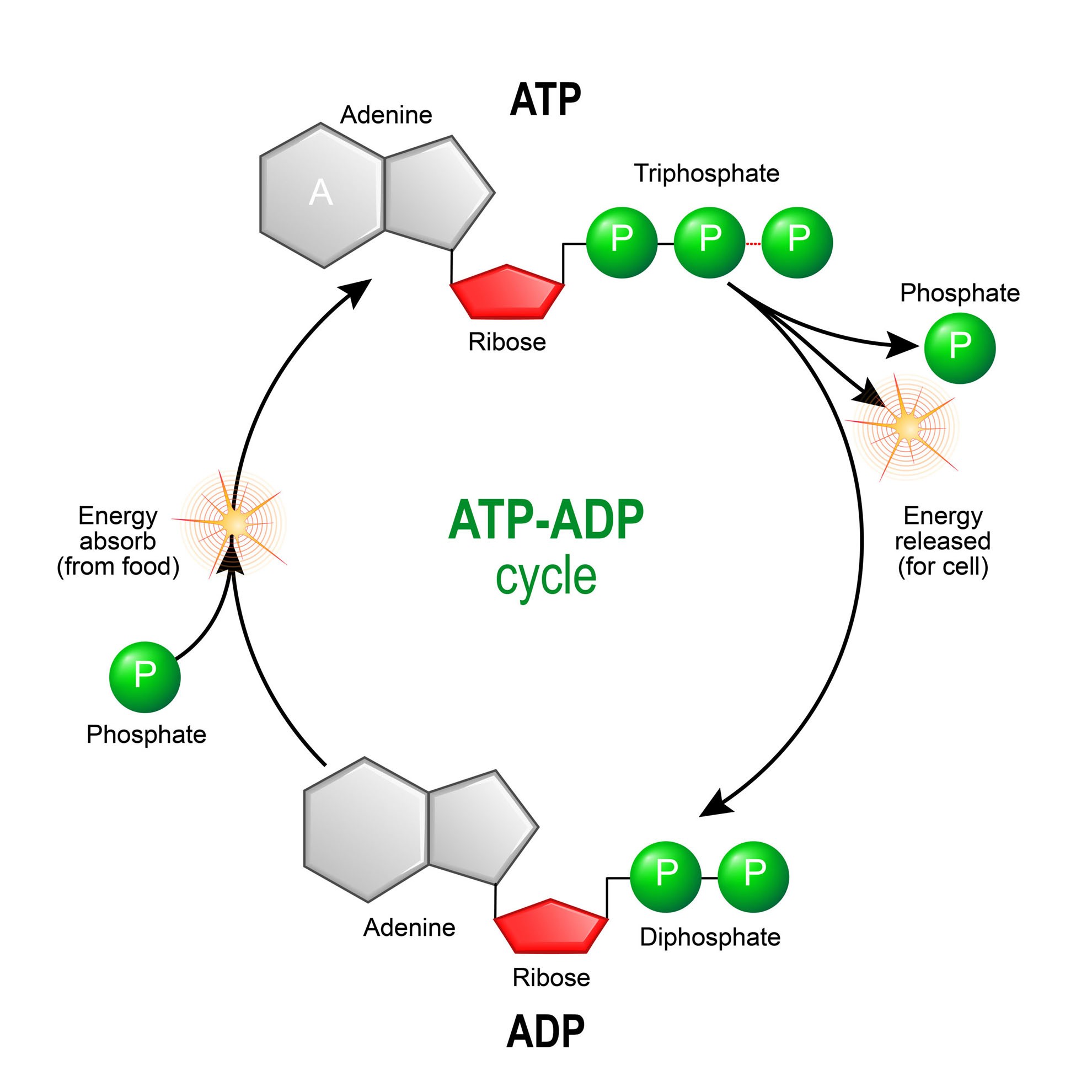
ATP: How It Works, How It's Made, and Why It's Important - Verywell Health ATP is a high-energy molecule with three phosphate bonds; ADP is low-energy with only two phosphate bonds. The Twos and Threes of ATP and ADP Adenosine tri phosphate (ATP) becomes adenosine di phosphate (ADP) when one of its three phosphate molecules breaks free and releases energy ("tri" means "three," while "di" means "two").
Label atp and adp molecules
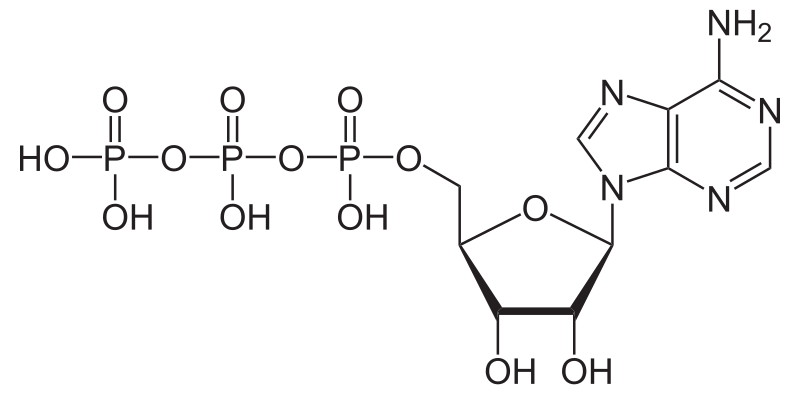
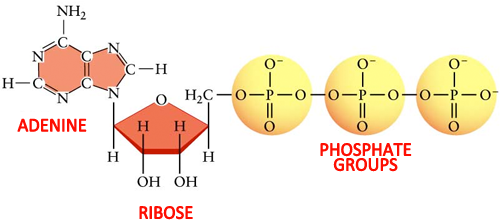
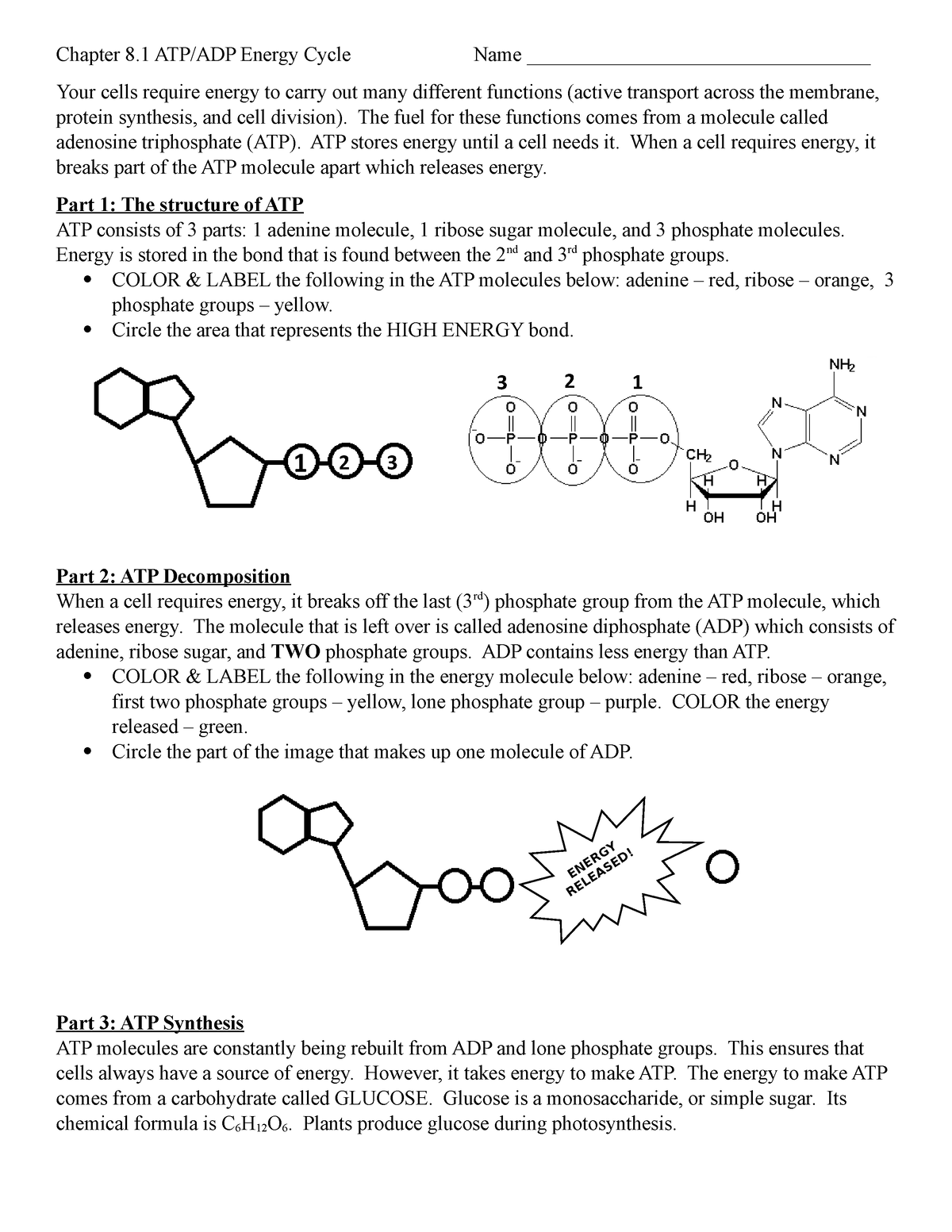
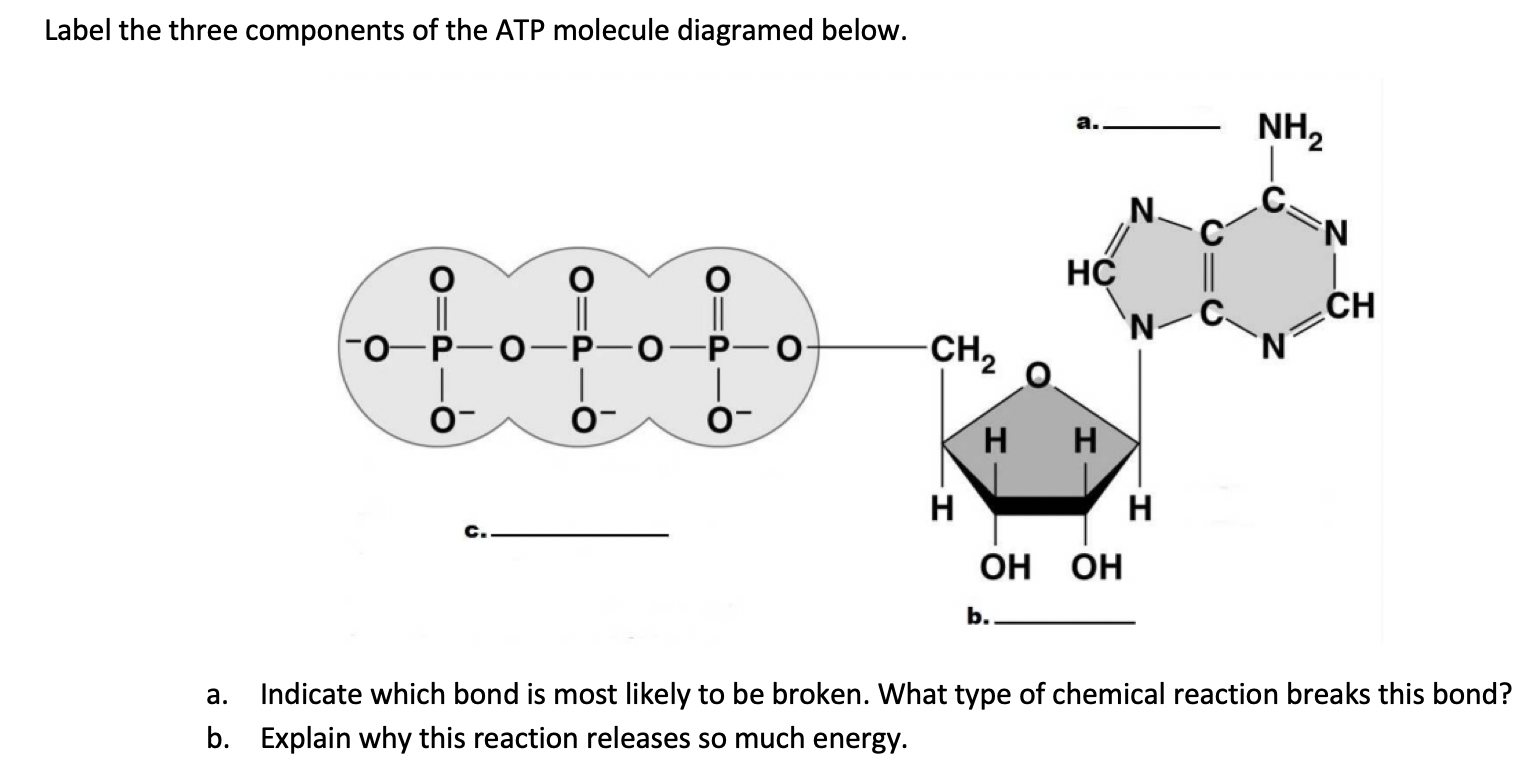
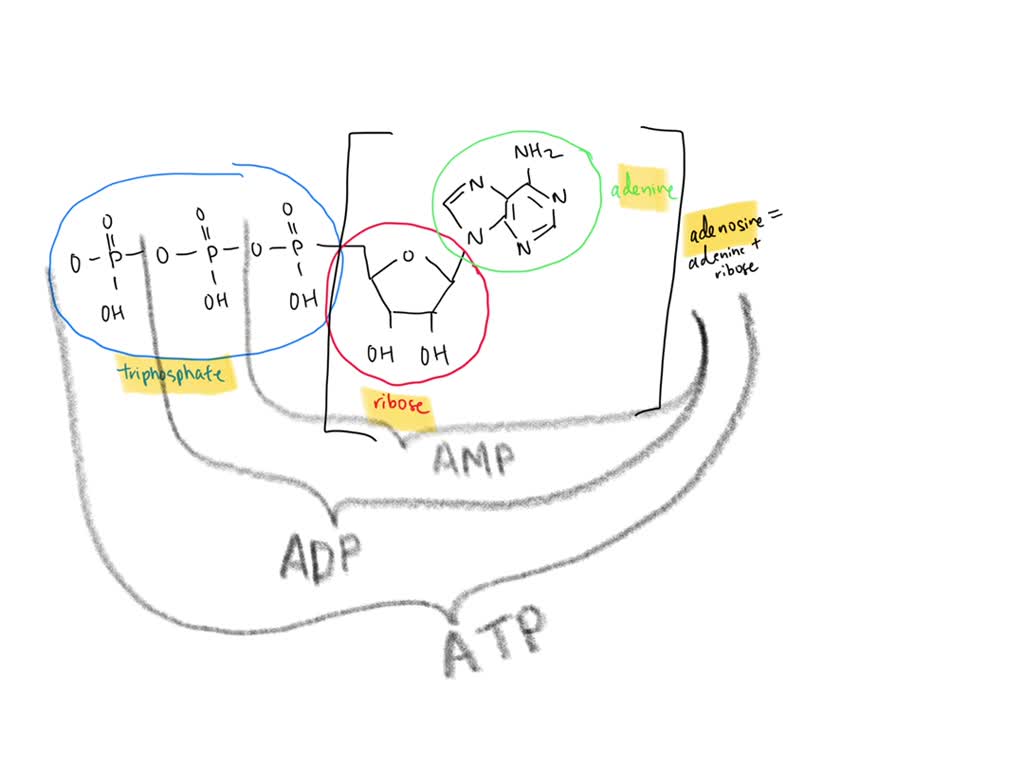
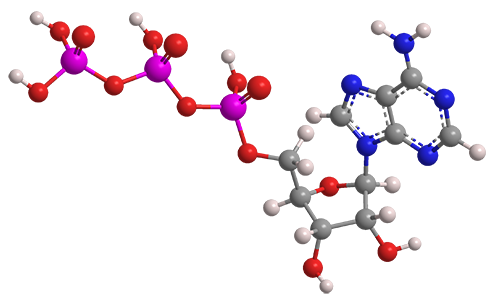
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenine is also found in DNA, and its incorporation is very similar, except ATP is converted into the form deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) before becoming part of a DNA strand. ATP, ADP, AMP, cAMP. Other molecules are related to ATP and have similar names, such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and cyclic AMP (cAMP). ATP & ADP - Biological Energy - Biology Online Tutorial ATP stands for a denosine t riphos p hat e, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of an adenosine molecule and three inorganic phosphates. After a simple reaction breaking down ATP to ADP, the energy released from the breaking of a molecular bond is the energy we use to keep ourselves alive. ATP and ADP cycle - EXAMPLE - 1 23 Chapter 8 ATP/ADP Energy ... - Studocu Part 1: The structure of ATP ATP consists of 3 parts: 1 adenine molecule, 1 ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. Energy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. COLOR & LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, 3 phosphate groups - yellow.
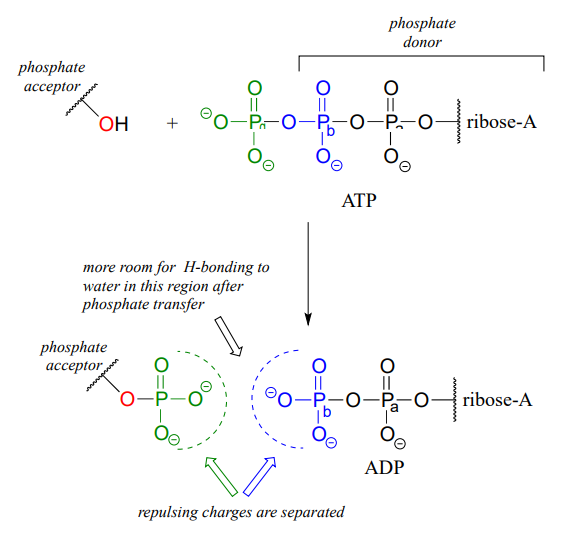
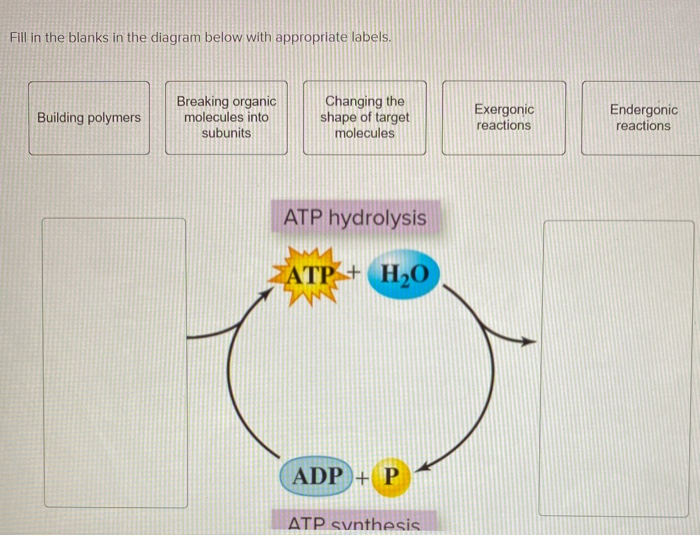
Label atp and adp molecules. ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Updated on May 09, 2019. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed. 9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor The most important donor of phosphate groups in the cell is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate, commonly known by its abbreviation ATP. that there are essentially three parts to the ATP molecule: an adenine nucleoside 'base', a five-carbon sugar (ribose), and triphosphate. The three phosphates are designated by Greek letters a, b, and g ... ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure and hydrolysis Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ADP also called adenosine diphosphate, is a molecule formed in living cells. It is often converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a high-energy molecule used in various biochemical reactions....
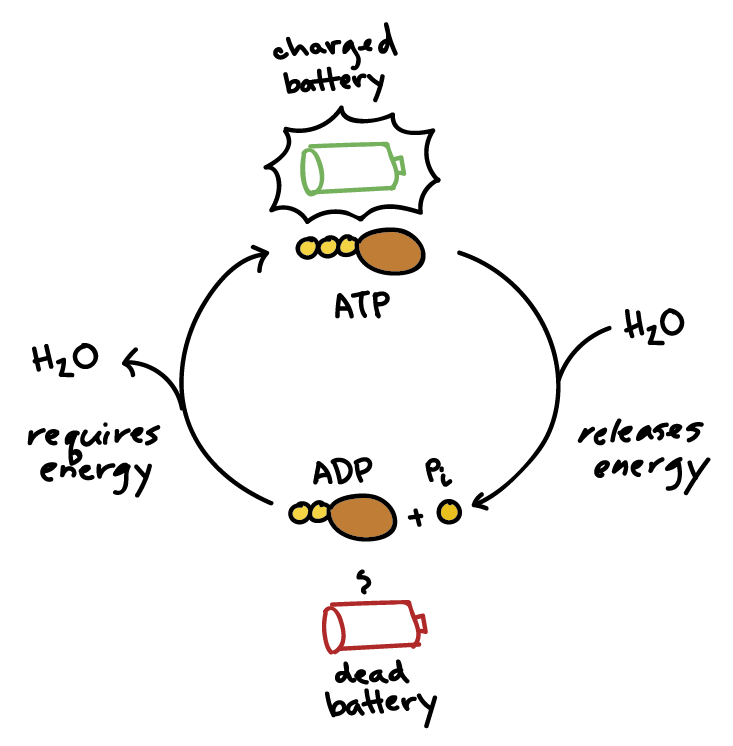
Difference Between ATP and ADP ATP and ADP are energy molecules that are found in all living organisms including the simplest forms to the highest. They are constantly recycled in the cells for energy storage and release. ATP and ADP are composed of three components known as adenine base, ribose sugar and phosphate groups. DOCX ATP consists of 3 parts: 1 adenine molecule, 1 ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. Energy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. COLOR & LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, 3 phosphate groups - yellow. 3 2 1 1 2 3 Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy In glycolysis, the beginning process of all types of cellular respiration, two molecules of ATP are used to attach 2 phosphate groups to a glucose molecule, which is broken down into 2 separate 3-carbon PGAL molecules. PGAL releases electrons and hydrogen ions to the electron carrier molecule NADP+. ATP/ADP - Chemistry LibreTexts ATP is an unstable molecule which hydrolyzes to ADP and inorganic phosphate when it is in equilibrium with water. The high energy of this molecule comes from the two high-energy phosphate bonds. The bonds between phosphate molecules are called phosphoanhydride bonds. They are energy-rich and contain a ΔG of -30.5 kJ/mol.
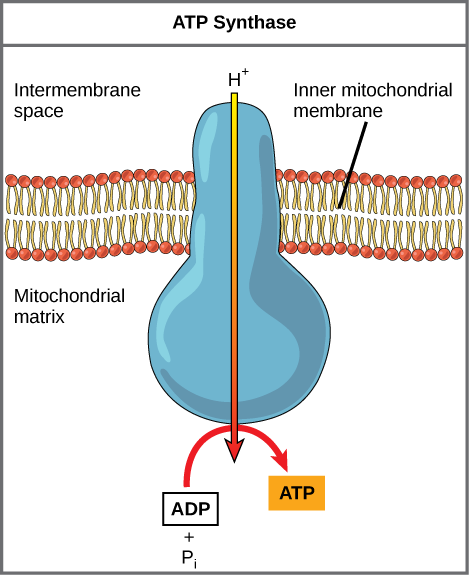
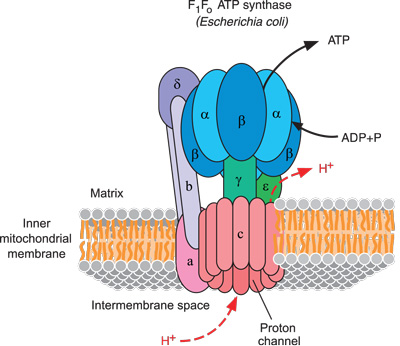
Electron Transport Chain | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning The end products of the electron transport chain are water and ATP. A number of intermediate compounds of the citric acid cycle can be diverted into the anabolism of other biochemical molecules, such as nonessential amino acids, sugars, and lipids. These same molecules can serve as energy sources for the glucose pathways. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ... ATP - powering the cell - Cellular respiration - BBC Bitesize ADP can be recharged back into ATP by adding a phosphate. This requires energy. These molecules can be recycled so that a constant stream of energy rich ATP is available for all metabolic pathways ... ATP and ADP cycle - EXAMPLE - 1 23 Chapter 8 ATP/ADP Energy ... - Studocu Part 1: The structure of ATP ATP consists of 3 parts: 1 adenine molecule, 1 ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. Energy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. COLOR & LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, 3 phosphate groups - yellow.
ATP & ADP - Biological Energy - Biology Online Tutorial ATP stands for a denosine t riphos p hat e, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of an adenosine molecule and three inorganic phosphates. After a simple reaction breaking down ATP to ADP, the energy released from the breaking of a molecular bond is the energy we use to keep ourselves alive.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenine is also found in DNA, and its incorporation is very similar, except ATP is converted into the form deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) before becoming part of a DNA strand. ATP, ADP, AMP, cAMP. Other molecules are related to ATP and have similar names, such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and cyclic AMP (cAMP).















![Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP ...](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/887889_ba7e3b5cc09d418996079c2f5db4b569.png)


Post a Comment for "40 label atp and adp molecules"